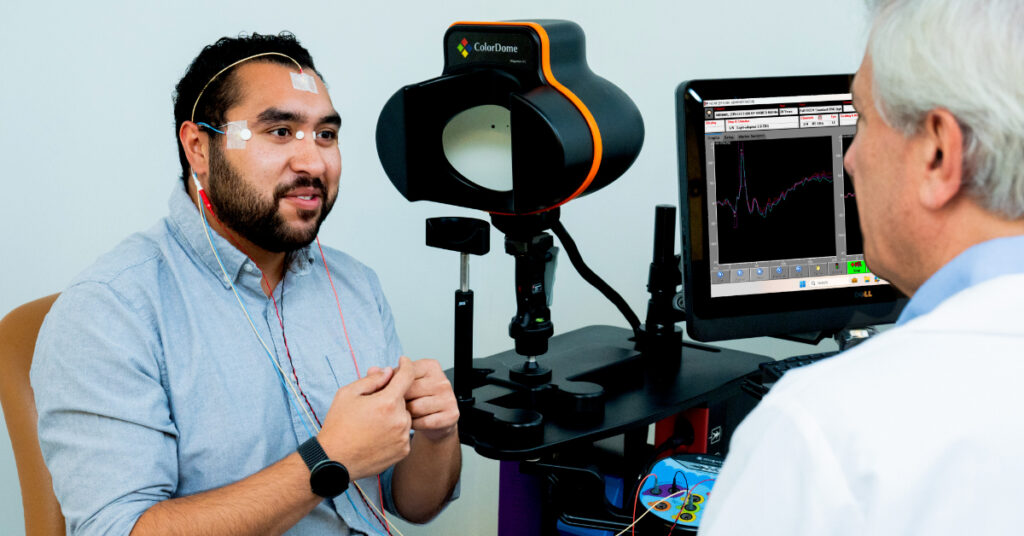
General Ophthalmology
With visual electrophysiology you can:
- Detect and monitor macular degeneration with longitudinal studies
- Screen for retinal toxicity from Plaquenil and other medications
- Assess damage from diabetic retinopathy
- Diagnose genetic vision conditions
Retina Specialty
With visual electrophysiology and psychophysics, you can:
- Identify specific inherited retinal disorders (IRDs)
- Establish disease severity and progression
- Assess impact of therapies
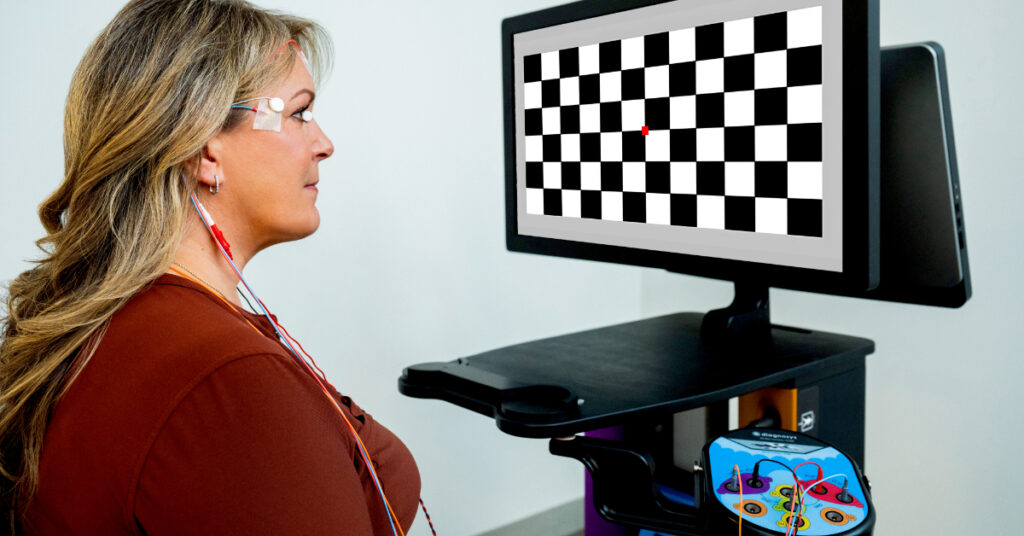


Glaucoma Specialty
Visual electrophysiology can:
- Establish baseline measurements once high intraocular pressure is detected
- Provide objective functional testing to complement structural imaging
- Provide additional information to help diagnose, manage, and track treatment efficacy of glaucoma
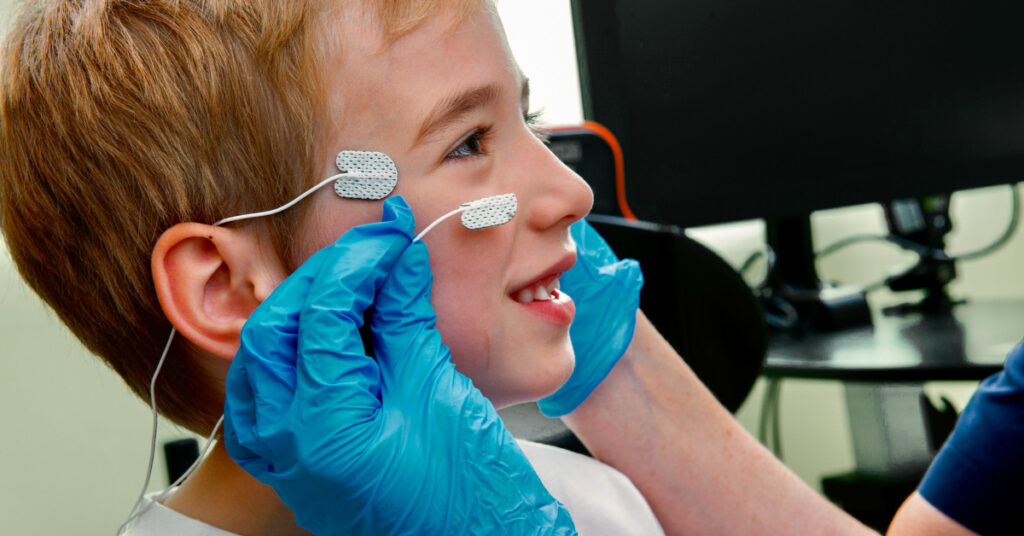
Pediatric Ophthalmology
Visual electrophysiology can inform the treatment of:
- Children suspected of hereditary retinal conditions
- Children who exhibit poor vision or poor visual behavior
- Children showing symptoms of nyctalopia, photophobia, or difficulty adjusting to light conditions
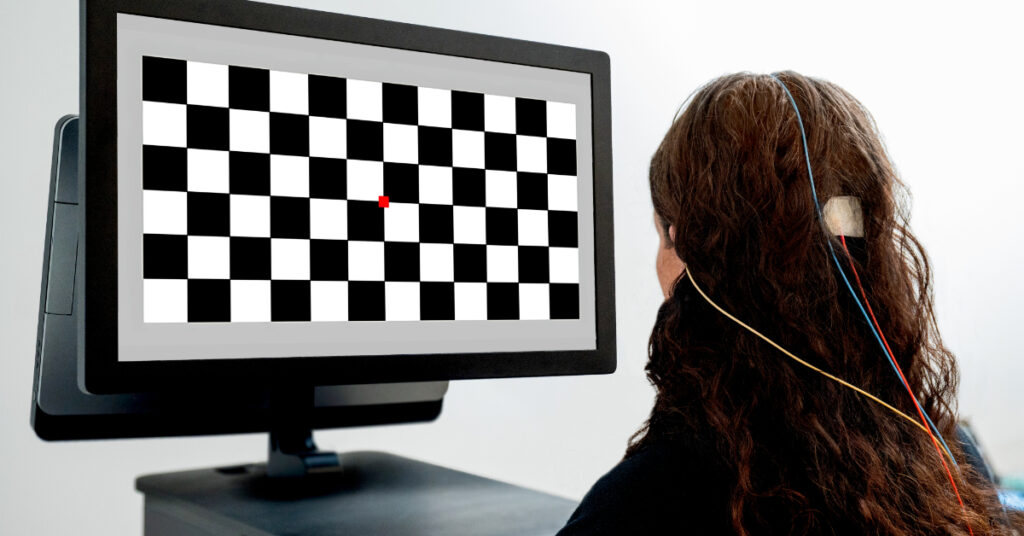

Neuro-Ophthalmology
Visual electrophysiology can:
- Distinguish between optic nerve diseases, retinal diseases, and functional vision loss
- Identify and monitor damage to the optic nerve
- Examine unexplained vision loss
- Be used as biomarkers for neurodegenerative diseases
